Knee Replacement Surgeon in Nagpur
Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee surgery is a medical intervention designed to address issues related to the knee joint, including pain, injuries, or degenerative diseases that have not improved with conservative treatment methods. The procedures can vary from minimally invasive techniques to more intricate surgeries, depending on the specific condition being treated. Among the various types of knee surgeries, knee replacement is the most prevalent; however, other interventions such as arthroscopy and ligament repair are also conducted for different knee-related ailments.
Types of Knee Surgery
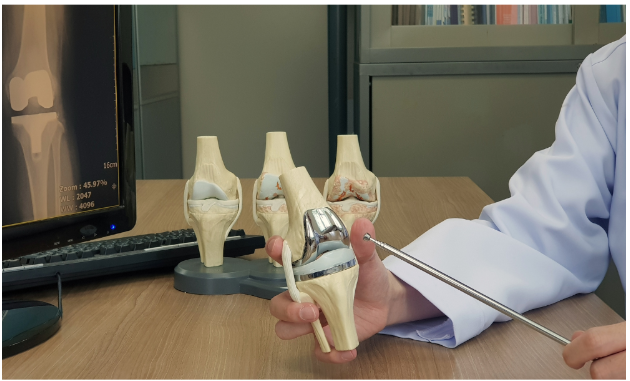
Knee Replacement Surgery (Arthroplasty)
Knee replacement, referred to as arthroplasty, is one of the most frequently performed knee surgeries. It is advised when the knee joint has sustained significant damage due to conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or trauma, leading to pain, stiffness, and restricted movement. There are two primary forms of knee replacement:
Total Knee Replacement
This procedure entails the complete replacement of the knee joint, including the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), and patella (kneecap). It is generally indicated when there is extensive joint damage.
Partial Knee Replacement
This approach involves replacing only the affected portion of the knee joint, making it a viable option when the damage is confined to a specific area. It typically results in a faster recovery and reduced postoperative discomfort compared to total knee replacement.
Knee Arthroscopy
Knee arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique employed for the diagnosis and treatment of various knee disorders. During this procedure, a small camera known as an arthroscope is inserted through small incisions, enabling the surgeon to visualize the interior of the knee joint on a monitor. This allows for the removal of damaged tissue, repair of ligaments, or extraction of debris such as bone fragments or deteriorated cartilage.
Common conditions addressed through arthroscopy include:
Torn cartilage (meniscus)
Ligament injuries (ACL, PCL tears)
Patellar misalignment
The benefits of arthroscopy encompass smaller incisions, reduced scarring, a lower risk of infection, and a faster recovery period compared to conventional open surgery.
- Ligament and Tendon Repair: Surgical interventions for ligament or tendon injuries, such as an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear, frequently necessitate reconstruction or repair. In ACL reconstruction, the injured ligament is substituted with a graft, which is usually harvested from the patient’s own body or a donor. This procedure is often essential for athletes or individuals engaged in high-impact sports who sustain ligament tears.
- Osteotomy:
An osteotomy is a surgical intervention that involves cutting a portion of the bone to realign the knee joint. This procedure is typically indicated in cases of early-stage osteoarthritis, particularly when the damage is localized to one side of the knee. The primary objective of an osteotomy is to redistribute the weight load from the affected area of the joint to a healthier region, thereby delaying or potentially averting the necessity for a total knee replacement.
Indications for Knee Surgery
Knee surgery is typically advised when conservative measures, such as physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle changes, do not provide sufficient symptom relief. Common indications for knee surgery include:
- Osteoarthritis: This degenerative joint condition results in the deterioration of cartilage, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune condition that can result in persistent inflammation and damage to the knee joint.
- Knee Injuries: Injuries such as fractures, ligament tears, and meniscal damage can cause instability, pain, and reduced mobility.
- Chronic Pain and Disability: When knee pain and associated disability significantly hinder daily activities and diminish quality of life, surgical intervention may be warranted.
Benefits of Knee Surgery
The primary advantages of knee surgery encompass:
- Pain Relief: Knee surgery is notably effective in alleviating chronic knee pain stemming from arthritis or injury.
- Improved Mobility: For the majority of patients, surgery enhances mobility and facilitates a return to regular activities, including walking, climbing stairs, and, in certain instances, running or engaging in sports.
- Restored Function: Procedures such as knee replacements restore the functionality of the joint, enabling individuals to regain independence and enhance their overall quality of life.
Risks and Complications
Knee surgery, like any surgical intervention, presents certain risks and complications. These may encompass:
- Infection: While uncommon, there is a possibility of infections occurring at the incision site or within the joint.
- Blood Clots: The risk of blood clots, particularly deep vein thrombosis (DVT), may increase following knee surgery, posing a serious threat if a clot travels to the lungs (pulmonary embolism).
- Implant Failure: In knee replacement procedures, implants may deteriorate over time, necessitating revision surgery.
- Stiffness and Pain: Some patients may encounter stiffness, ongoing pain, or a reduced range of motion post-surgery.
- Anesthesia Risks: Anesthesia carries inherent risks, especially for older individuals or those with pre-existing health issues.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
The recovery timeline following knee surgery varies based on the specific procedure performed and the patient’s overall health status.
Typically, recovery includes:
- Postoperative Care: This may involve pain management through medications, applying ice to the knee, and maintaining the knee in an elevated position.
- Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation plays a vital role in recovery, concentrating on regaining strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the knee. Patients usually start with gentle exercises and gradually advance to more demanding activities as healing progresses.
- Gradual Return to Activities: It is crucial to refrain from high-impact activities during the initial recovery phase to ensure complete healing of the knee. Eventually, most patients can resume walking, swimming, cycling, and other low-impact exercises.